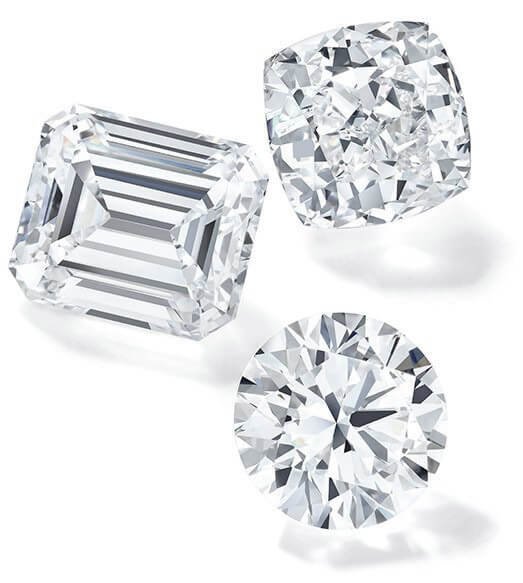
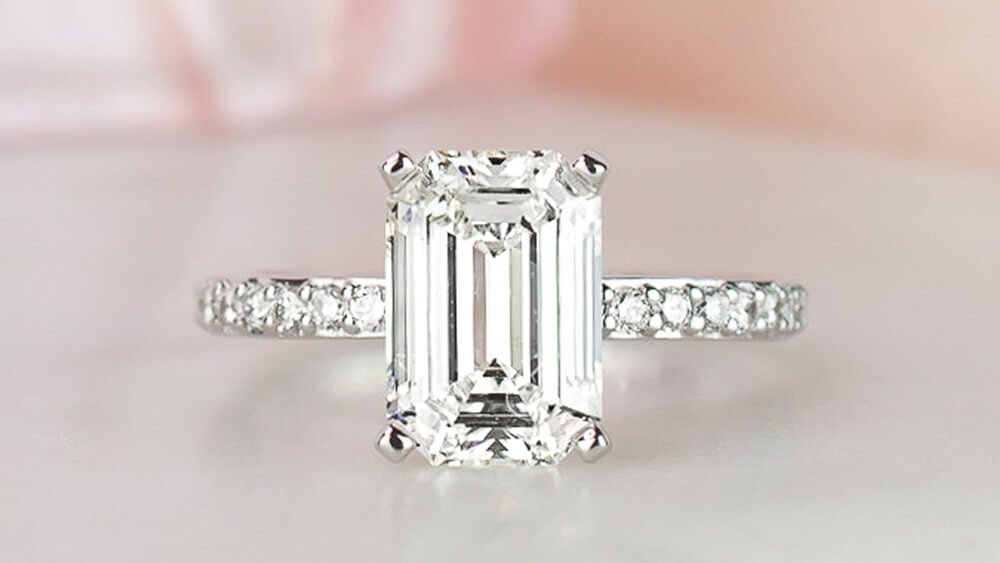
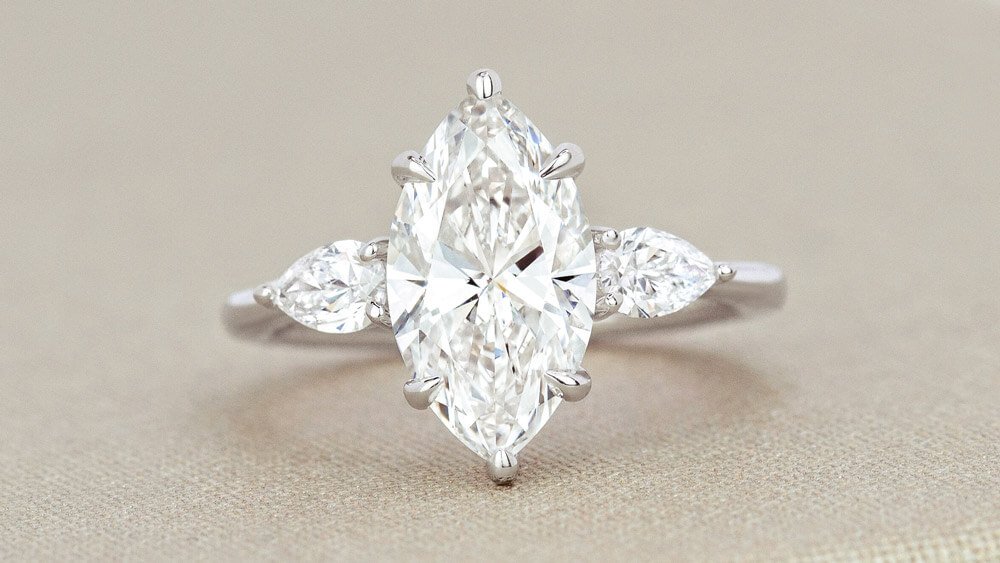
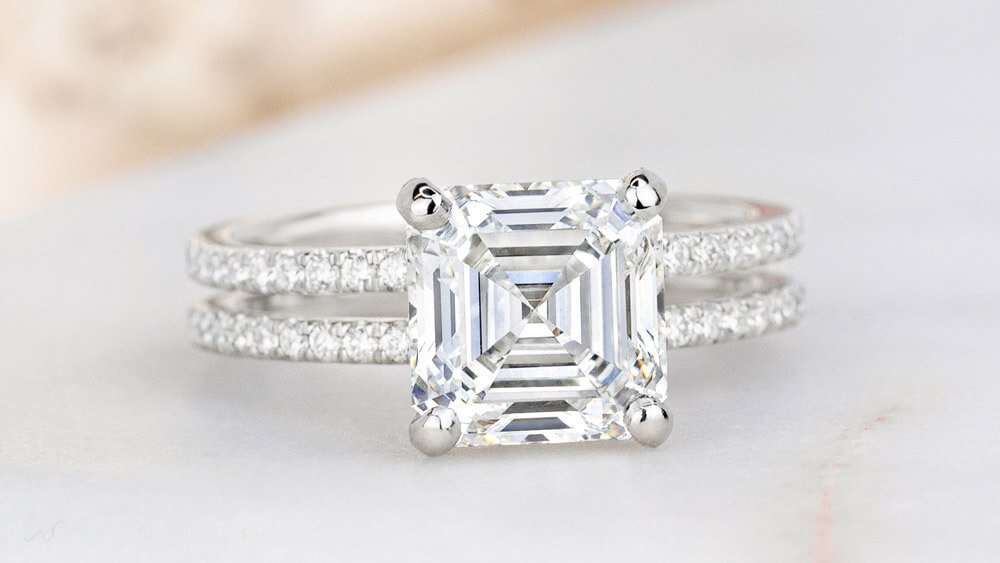
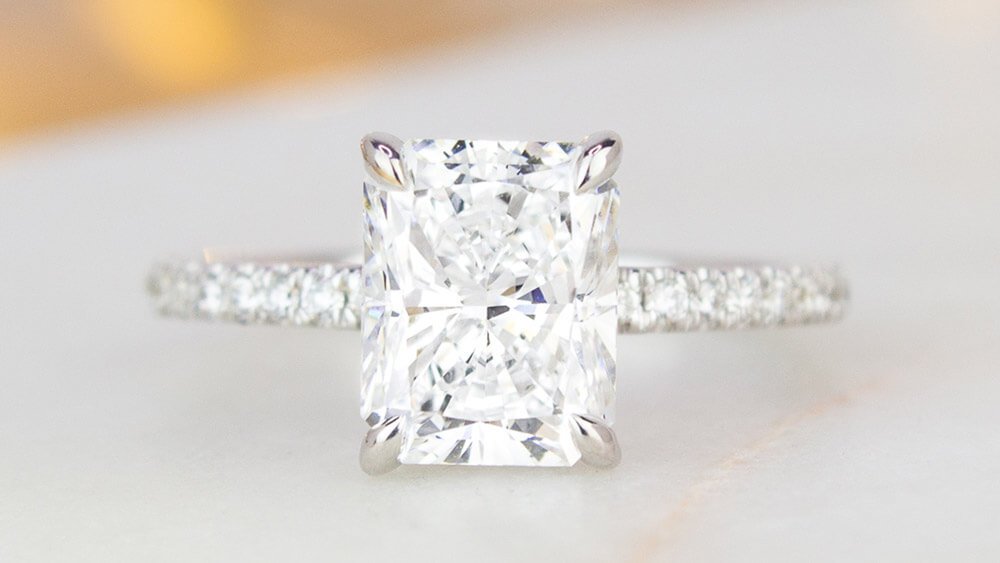
What is Diamond Shape?
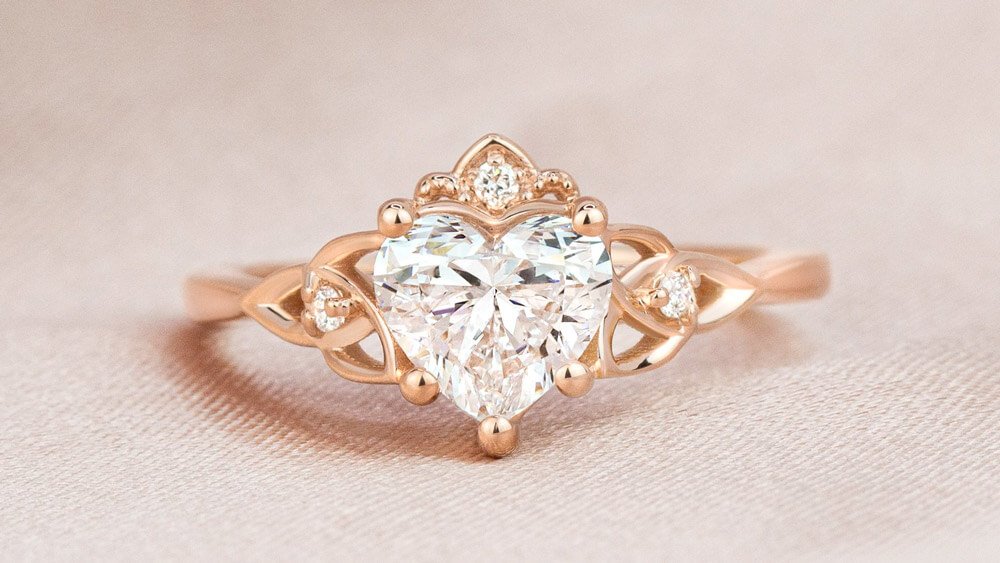
Diamond shape refers to the outline of your diamond. It’s thephysical and visual shape of the stone. Every diamond shape has unique attributes that impact its sparkle and overall look.
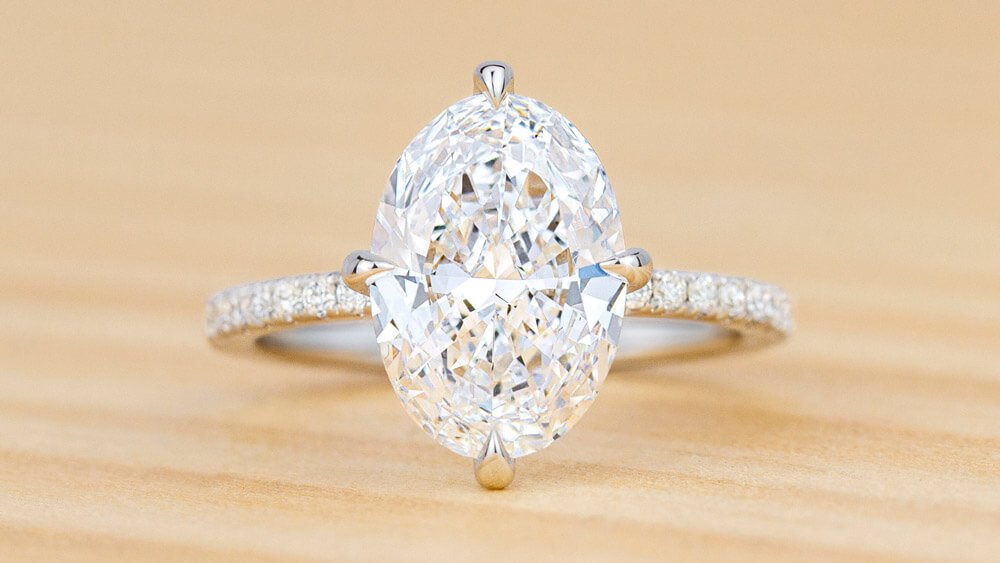
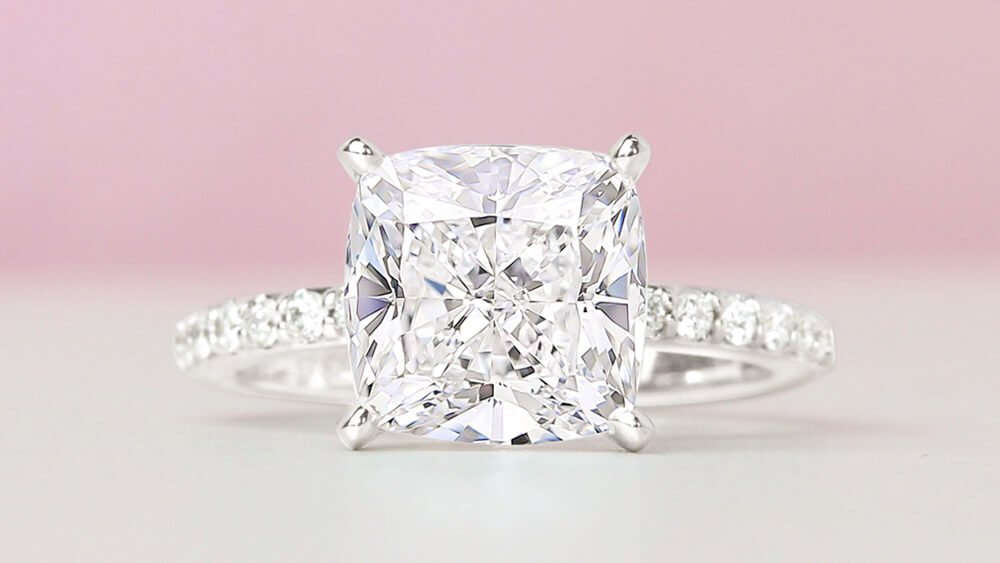
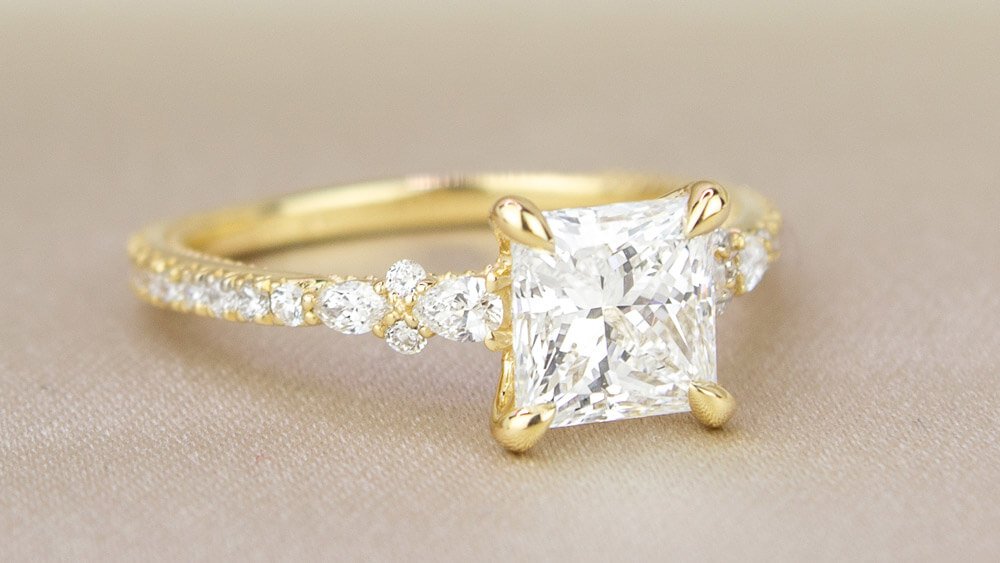
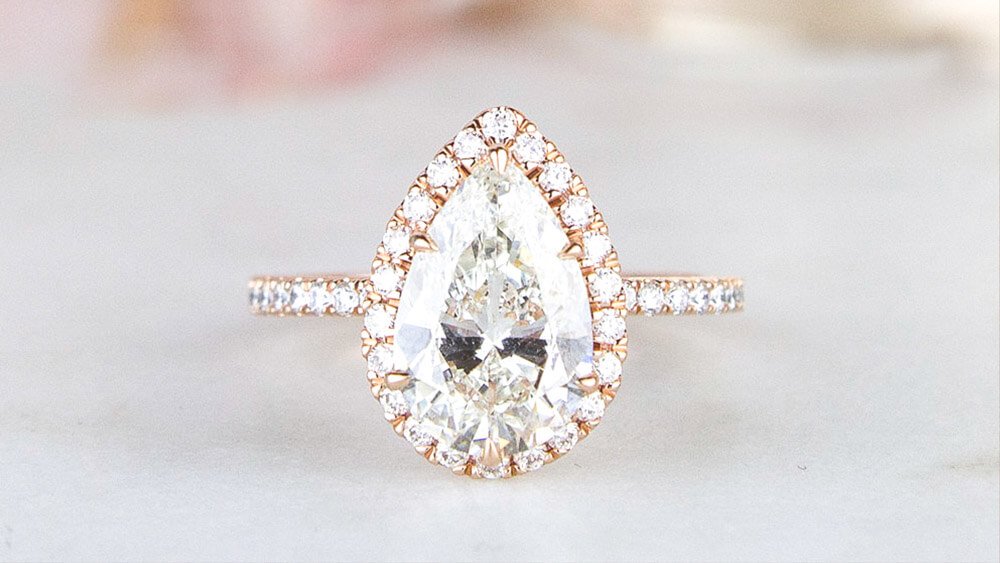
Shape is often one of the first attributes that couples consider when shopping for a diamond. While round diamonds are the most popular choice, many couples are also drawn to the distinctive look of non-round, or “fancy shaped” diamonds. Fancy shaped diamonds includeoval, cushion, princess, pear, emerald, marquise, asscher, radiant, and heart shaped diamonds.
Diamond shape refers to the outline of your diamond. It’s thephysical and visual shape of the stone. Every diamond shape has unique attributes that impact its sparkle and overall look.
Shape is often one of the first attributes that couples consider when shopping for a diamond. While round diamonds are the most popular choice, many couples are also drawn to the distinctive look of non-round, or “fancy shaped” diamonds. Fancy shaped diamonds includeoval, cushion, princess, pear, emerald, marquise, asscher, radiant, and heart shaped diamonds.
Are Diamond Cut and Diamond Shape the Same Thing?
Though there’s a difference between shape and cut, many jewelers use the terms interchangeably. The shape is the silhouette of the stone, while the cut refers to how the light hits the facets.
Precise cuts ensure diamonds reflect light and sparkle. Professional gemologists grade a diamond’s cut by analyzing seven components: brightness, dispersion, scintillation, weight ratio, durability, polish, and symmetry. Learn more about these seven components in our diamond cuts guide.
Diamond shape describes the outline of the diamond itself. When you look at the diamond, you can discern its shape quickly. It takes a more experienced eye to notice the cut because you have to take in the facets, reflective qualities, and overall proportions of the diamond.
You can choose any shape for a diamond and then get a specific cut, like super ideal, ideal, very good, etc. No matter what cut you choose, you can still have a certain shape for the diamond.
Though there’s a difference between shape and cut, many jewelers use the terms interchangeably. The shape is the silhouette of the stone, while the cut refers to how the light hits the facets.
Precise cuts ensure diamonds reflect light and sparkle. Professional gemologists grade a diamond’s cut by analyzing seven components: brightness, dispersion, scintillation, weight ratio, durability, polish, and symmetry. Learn more about these seven components in our diamond cuts guide.
Diamond shape describes the outline of the diamond itself. When you look at the diamond, you can discern its shape quickly. It takes a more experienced eye to notice the cut because you have to take in the facets, reflective qualities, and overall proportions of the diamond.
You can choose any shape for a diamond and then get a specific cut, like super ideal, ideal, very good, etc. No matter what cut you choose, you can still have a certain shape for the diamond.
Ideal Length-to-Width (L:W) Ratio for Each Diamond Shape
A factor that is often overlooked is the length-to-width ratio of a diamond. It’s different for each diamond shape, but in general, the length-to-width ratio gives diamonds a look of symmetry.
- Round: Since round diamonds are close to a perfect circle, the ideal ratio is 1 because the length and width should be the same. Most brilliant cut round diamonds have a ratio of 1 or 1.03.
- Oval: Oval diamonds are slightly elongated because, otherwise, they’d look round. The typical oval length-to-width ratio ranges between 1.3 to 1.5. Diamonds closer to the 1.3 ratios are rounder and get longer as they edge closer to 1.5.
- Pear: Like oval diamonds, pear diamonds have a higher ratio because they’re longer. The ratio for pear diamonds can range from 1.4 up to 1.7 since they have a thicker bottom.
- Princess: The ideal ratio for princess diamonds ranges from 1 to 1.04. This ratio gives them a sturdy square appearance while letting the sharp corners capture shine.
- Emerald: An emerald-shaped diamond is unique because of how the facets look. The diamond itself has a rectangular shape, but the facets catch the light and make the diamond look like a never-ending hall of mirrors. The ideal ratio for emerald cut diamonds ranges from 1.3 to 1.45.
- Marquise: Marquise diamonds have a breathtaking look, with the long elliptical diamond giving your engagement ring a timeless look. The ideal ratio for marquise diamonds is the highest on the list due to the stone’s length. You’ll find most marquise shapes with ratios starting at 1.85 to 2.1.
- Asscher: Asscher diamonds have a ratio close to that of a princess. A 1 ratio is ideal, but you might find variations up to 1.05. This allows the square shape to provide a sturdy base, so the unique octagonal look will catch everyone’s attention.
- Cushion: A cushion diamond can be square, but it often has a slightly higher ratio, giving it a rectangular shape. Even a ratio of 1.14 is more rectangular than square.
- Radiant: A radiant diamond is a popular choice for an engagement ring because you can customize the look depending on the ratio. A longer, narrower rectangle will have a ratio of 1.35 or higher.
- Heart: The ratio for a heart shaped diamond is close to 1 because symmetry is crucial.
A factor that is often overlooked is the length-to-width ratio of a diamond. It’s different for each diamond shape, but in general, the length-to-width ratio gives diamonds a look of symmetry.
Why Length-to-Width Ratio Matters
Length-to-width ratio matters because it impacts how your diamond looks and can change the overall aesthetic of your ring.
A length-to-width ratio of 1 tells you that the diamond is perfectly symmetrical, as in the case of square cut, round cut, and heart shaped diamonds. Anything higher than one is an elongated diamond that covers more of your finger. Anything less will cover more of the band.
Having an ideal length-to-width ratio isn’t a necessity, but understanding the basics helps you picture what your engagement ring will look like.Anything outside of the ideal length-to-width ranges might change the brilliance and cut of the diamond. So, if the proportions of a diamond are too far off, you could potentially lose some sparkle if the diamond facets can’t catch the light in the right way.
But there’s no set length-to-width ratio you need to shop for; the right ratio for your diamond jewelry depends entirely on personal preference and how you want your diamonds to look.
Length-to-width ratio matters because it impacts how your diamond looks and can change the overall aesthetic of your ring.
A length-to-width ratio of 1 tells you that the diamond is perfectly symmetrical, as in the case of square cut, round cut, and heart shaped diamonds. Anything higher than one is an elongated diamond that covers more of your finger. Anything less will cover more of the band.
Having an ideal length-to-width ratio isn’t a necessity, but understanding the basics helps you picture what your engagement ring will look like.Anything outside of the ideal length-to-width ranges might change the brilliance and cut of the diamond. So, if the proportions of a diamond are too far off, you could potentially lose some sparkle if the diamond facets can’t catch the light in the right way.
But there’s no set length-to-width ratio you need to shop for; the right ratio for your diamond jewelry depends entirely on personal preference and how you want your diamonds to look.
How Diamond Shape Affects Price
Diamond shape affects price just as the 4Cs do. Anything impacting the diamond’s appearance will change the price. For example, the diamond’s length-to-width ratio can also affect the price. Anything beyond the typical range of your diamond shape is rare, so the price will adjust accordingly.
Round diamonds are so popular that the market price is higher than unique shapes. But there’s more to the cost that happens behind the scenes. The manufacturing process requires more of the rough diamond to make the perfect round shape, so you’re paying for that precision. And cutting a rough diamond into a round shape discards more diamond chips, so you’re paying for what isn’t usable in other jewelry.
Princess cut diamonds are second to round, so the price is still high, though they’re more affordable than round cut diamonds. This is because, in the manufacturing process, they use about 80% of the rough diamond to cut into a princess shape.
Radiant, emerald, cushion, and asscher cut diamonds are more affordable because they use most of the rough diamonds. Choosing a fancy-shaped diamond not only means you’ll enjoy a unique ring but also that you’re discarding fewer diamond chips and saving money, all at the same time.
Diamond shape affects price just as the 4Cs do. Anything impacting the diamond’s appearance will change the price. For example, the diamond’s length-to-width ratio can also affect the price. Anything beyond the typical range of your diamond shape is rare, so the price will adjust accordingly.
Round diamonds are so popular that the market price is higher than unique shapes. But there’s more to the cost that happens behind the scenes. The manufacturing process requires more of the rough diamond to make the perfect round shape, so you’re paying for that precision. And cutting a rough diamond into a round shape discards more diamond chips, so you’re paying for what isn’t usable in other jewelry.
Princess cut diamonds are second to round, so the price is still high, though they’re more affordable than round cut diamonds. This is because, in the manufacturing process, they use about 80% of the rough diamond to cut into a princess shape.
Radiant, emerald, cushion, and asscher cut diamonds are more affordable because they use most of the rough diamonds. Choosing a fancy-shaped diamond not only means you’ll enjoy a unique ring but also that you’re discarding fewer diamond chips and saving money, all at the same time.